1. Introduction to Web Hosting Types
In the digital age, establishing an online presence is essential for businesses and individuals alike. A critical component of this presence is selecting the right web hosting service, which serves as the foundation for your website's accessibility and performance. The primary web hosting options include shared hosting, Virtual Private Server (VPS) hosting, dedicated server hosting, and cloud hosting. Each offers distinct features, advantages, and considerations. Understanding these differences is vital to making an informed decision that aligns with your website's requirements and growth trajectory.![]()
2. Shared Hosting
Shared hosting is often the entry-level choice for individuals and small businesses launching their first websites. In this arrangement, multiple websites reside on a single physical server, collectively sharing its resources such as CPU, RAM, and storage. This communal setup is analogous to living in an apartment complex where residents share common facilities.
Key Features:
- Affordability: Shared hosting is cost-effective, making it accessible for those with limited budgets.
- Ease of Use: Hosting providers manage server maintenance, updates, and security, allowing users to focus on content creation and site management without technical complexities.
- Limited Resources: Since resources are shared among multiple users, high traffic on one site can impact the performance of others, a phenomenon known as the "noisy neighbor" effect.
Ideal For:
Shared hosting is suitable for personal blogs, small business websites, and portfolios that anticipate low to moderate traffic levels. It's an excellent starting point for those new to web hosting or with minimal technical expertise.
3. Virtual Private Server (VPS) Hosting
VPS hosting offers a middle ground between shared and dedicated hosting solutions. In this setup, a physical server is divided into multiple virtual compartments, each functioning as an independent server with dedicated resources. This isolation ensures that the performance of one VPS is unaffected by the activities of others on the same physical server.
Key Features:
- Dedicated Resources: Users have allocated amounts of CPU, RAM, and storage, ensuring consistent performance.
- Root Access: VPS hosting provides greater control over server configurations, allowing for custom software installations and settings.
- Scalability: Resources can be adjusted to accommodate growth, making it suitable for websites expecting increased traffic over time.
Ideal For:
VPS hosting is ideal for growing businesses, e-commerce platforms, and websites with moderate traffic that require more control and reliability than shared hosting can offer. It appeals to users with some technical knowledge or those willing to manage more complex server configurations.
4. Dedicated Server Hosting
Dedicated server hosting provides an entire physical server exclusively for one client. This arrangement offers unparalleled performance, control, and security, as all server resources are dedicated to a single website or application.
Key Features:
- Maximum Performance: With exclusive access to all server resources, websites can handle high traffic volumes and resource-intensive applications without performance degradation.
- Complete Control: Users have full administrative access to the server, allowing for customized configurations, software choices, and security measures tailored to specific needs.
- Enhanced Security: Isolation from other users reduces the risk of security breaches stemming from neighboring sites.
Ideal For:
Dedicated hosting is suited for large enterprises, high-traffic websites, and applications with stringent security and compliance requirements. It is best for users with advanced technical expertise or those who have access to IT professionals capable of managing and maintaining the server infrastructure.
5. Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting utilizes a network of interconnected servers to host websites and applications, distributing data and resources across multiple physical machines. This decentralized approach offers flexibility and resilience, as the failure of one server does not lead to downtime; other servers in the network can seamlessly take over.
Key Features:
- Scalability: Resources can be dynamically adjusted based on real-time demands, accommodating traffic spikes without affecting performance.
- Reliability: The distributed nature of cloud hosting ensures high availability and redundancy, minimizing the risk of data loss or downtime.
- Pay-as-You-Go Pricing: Users are billed based on actual resource usage, which can be cost-effective for websites with variable traffic patterns.
Ideal For:
Cloud hosting is ideal for websites and applications experiencing fluctuating traffic, startups anticipating rapid growth, and businesses seeking a balance between performance and cost-efficiency. It appeals to users who prefer a flexible hosting environment without the need to manage physical hardware.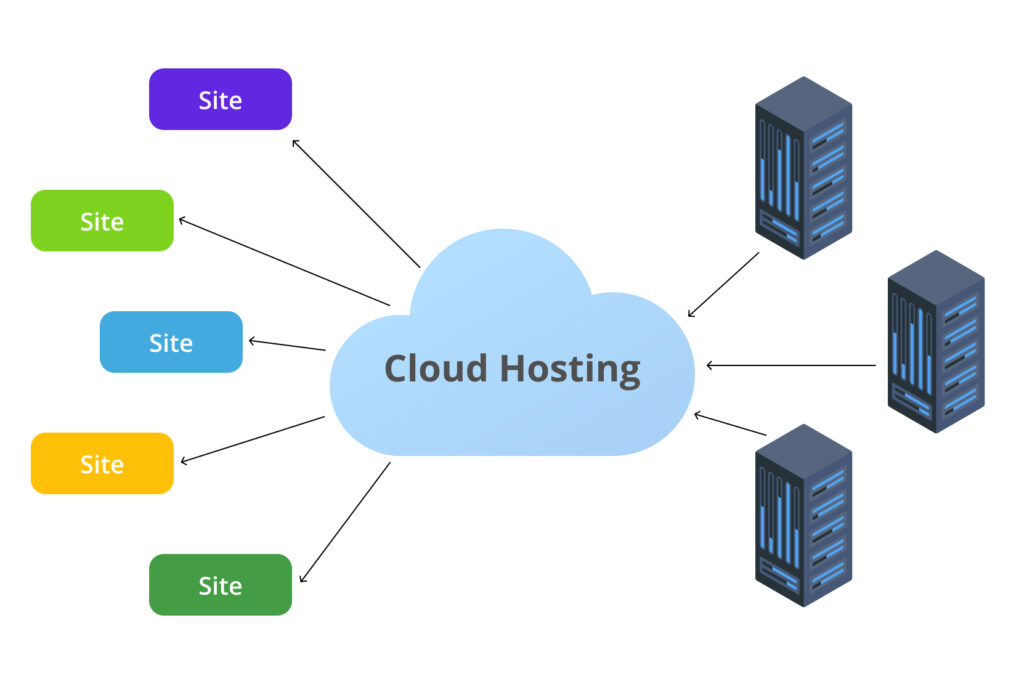
6. Comparative Analysis
Understanding the distinctions between these hosting types is essential for making an informed decision. Below is a comparative overview:
| Feature | Shared Hosting | VPS Hosting | Dedicated Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Limited | Stable | High | Scalable |
| Resource Allocation | Shared | Dedicated | Exclusive | Distributed |
| Customization |



You must be logged in to post a comment.