1. Introduction to Restore Policies
A restore policy outlines how a hosting provider handles website recovery in case of accidental data loss, cyberattacks, or system failures. These policies define what data is backed up, how often backups are created, and how customers can request a site restoration.
Many businesses rely on their websites for daily operations, making a well-defined restore policy essential. Without a reliable restoration process, companies risk prolonged downtime, data loss, and financial setbacks. Before choosing a hosting provider, it’s crucial to understand their backup and restore policies to ensure website resilience.
2. Backup Retention and Storage Duration
One of the most critical aspects of a restore policy is the backup retention period—the duration for which backups are stored before being overwritten or deleted. Hosting providers typically offer:
- Daily backups (retained for 7–30 days)
- Weekly backups (retained for 1–3 months)
- Monthly backups (retained for 6–12 months)
Some providers allow users to create manual backups or offer premium plans with extended storage durations. Knowing the retention policy ensures users can recover data from an appropriate timeframe.
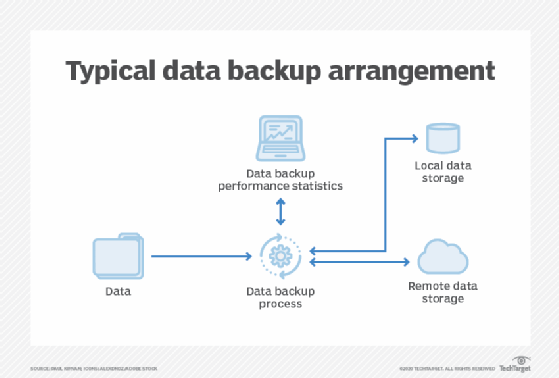
3. Restore Request Procedures
Different hosting providers have varying procedures for requesting a site restoration. The most common methods include:
- Self-service restore via control panel – Users can restore their site through a hosting dashboard.
- Support ticket-based restore – Customers submit a request to the provider’s support team.
- Automated restore services – Some providers offer one-click restores with minimal downtime.
Understanding the restore process helps businesses plan for potential recovery scenarios and reduces delays in website restoration.
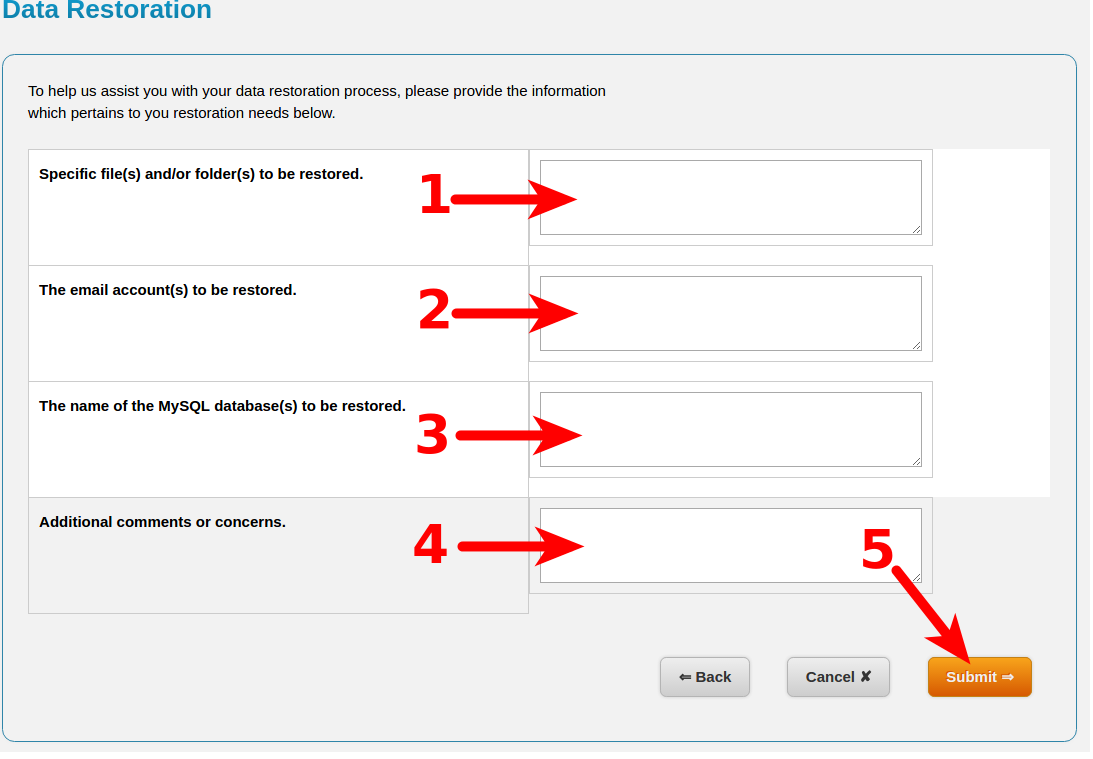
4. Timeframe and Service-Level Agreements (SLAs)
The speed of restoration depends on the hosting provider’s Service-Level Agreement (SLA). Common restore timeframes include:
- Instant or within minutes – For self-service backups
- Within 24 hours – For provider-assisted restorations
- Longer durations (48+ hours) – For extensive recovery cases requiring manual intervention
A provider’s SLA may include guarantees on restoration time, ensuring minimal downtime for mission-critical websites. Businesses should choose a provider with a fast and reliable recovery process.

5. Cost and Limitations of Restoration Services
Some hosting providers include free backup restoration in their plans, while others charge a fee based on factors like:
- The number of restores allowed per month
- The type of restore (full-site vs. database-only)
- Emergency or expedited restoration requests
Premium hosting plans may offer unlimited free restores, while budget plans may charge per request. Understanding cost implications helps businesses budget for potential recovery needs.
6. Self-Service vs. Provider-Assisted Restores
Restore policies often distinguish between self-service and provider-assisted restoration options:
- Self-service – Users restore backups using control panel tools (e.g., cPanel, Plesk). This method is quick but requires technical knowledge.
- Provider-assisted – The hosting provider’s team handles the restoration upon request. While convenient, it may involve delays and additional fees.
Choosing the right method depends on the user’s technical expertise and the level of control they want over the restoration process.
7. Best Practices for Website Backup and Restoration
To ensure seamless restoration in case of emergencies, businesses should follow best practices such as:
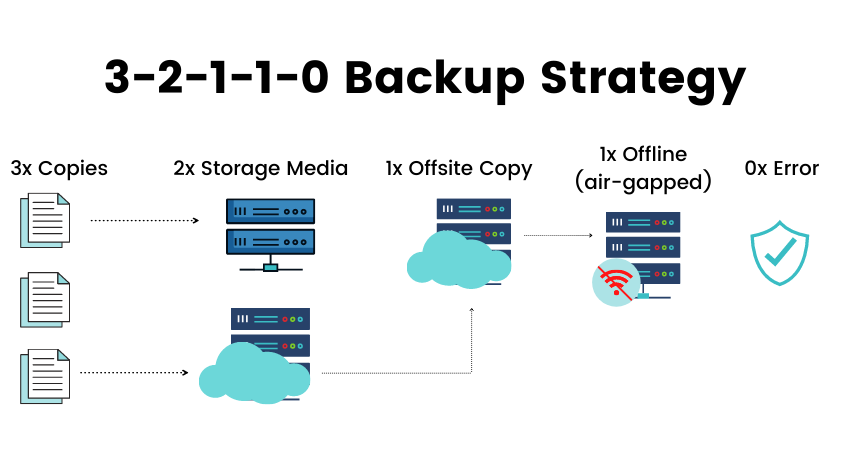
- Regularly scheduling backups – Even if a provider offers automated backups, manual backups add an extra layer of security.
- Storing backups externally – Keeping copies on cloud storage or local devices prevents complete data loss if the hosting provider experiences failures.
- Testing restore processes – Periodically testing backups ensures they are functional and can be restored without issues.
- Reviewing provider policies regularly – Hosting services update policies over time, so staying informed prevents unexpected surprises during recovery.


You must be logged in to post a comment.