1. Introduction to MySQL Management
MySQL is one of the most widely used relational database management systems (RDBMS), known for its scalability, reliability, and performance. It is used by websites, applications, and enterprises to store and retrieve structured data efficiently. Effective MySQL management ensures high availability, optimized query performance, and data security. This section introduces MySQL’s key features, its role in data management, and why proper administration is crucial for maintaining a reliable database infrastructure.

2. Installing and Configuring MySQL
Setting up MySQL correctly is the foundation of effective database management. The installation process varies depending on the operating system (Windows, Linux, or macOS). Essential steps include:
- Downloading and installing MySQL Server from the official MySQL website.
- Configuring user permissions and security settings during setup.
- Setting up MySQL Workbench for GUI-based management.
- Optimizing MySQL configuration files (my.cnf or my.ini) to enhance performance.
Proper installation and configuration ensure a stable and high-performing MySQL environment.

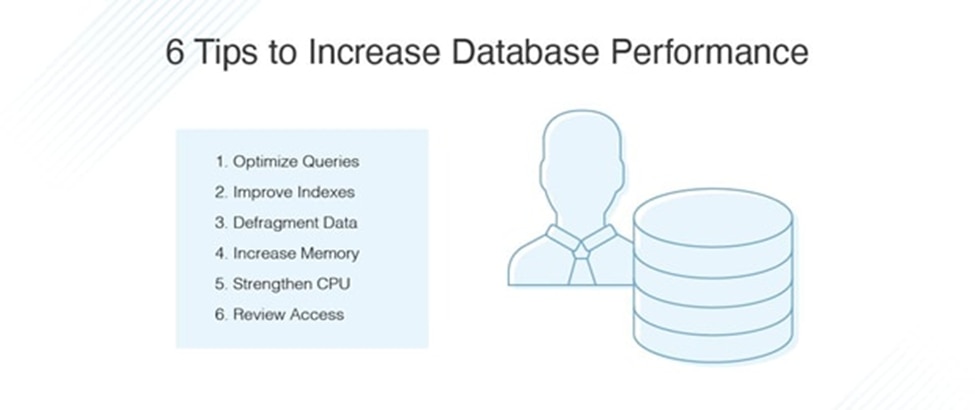
3. Optimizing Database Performance
Database performance optimization is crucial for handling large datasets efficiently. Key techniques include:
- Indexing: Creating indexes on frequently queried columns to speed up retrieval.
- Query Optimization: Using EXPLAIN to analyze and improve slow queries.
- Normalization: Structuring data to reduce redundancy and improve consistency.
- Caching: Implementing query caching to reduce load on the database server.
- Connection Pooling: Managing database connections efficiently to prevent bottlenecks.
By following these strategies, administrators can ensure faster query execution and improved resource utilization.
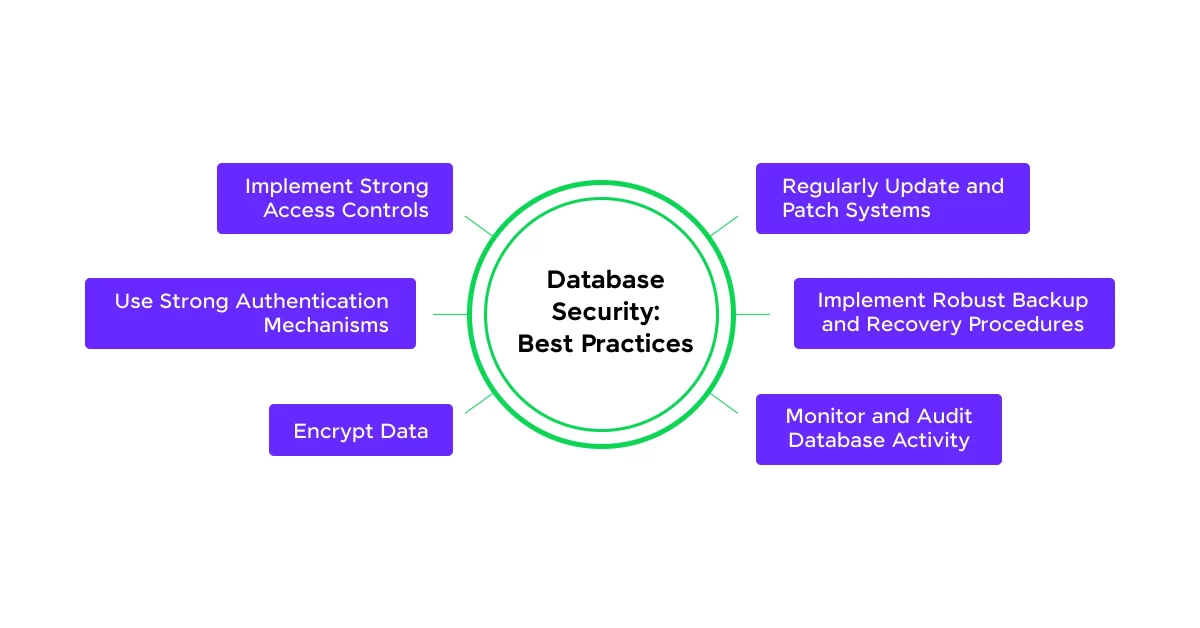
4. Securing MySQL: Best Practices for Data Protection
Security is a critical aspect of MySQL management to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Best practices include:
- Using Strong Authentication: Enforcing strong passwords and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Restricting Remote Access: Limiting MySQL access to trusted IP addresses.
- Regularly Updating MySQL: Keeping the database software up to date to patch vulnerabilities.
- Encrypting Data: Using SSL/TLS for secure data transmission.
- Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assigning user roles with appropriate privileges.
Securing MySQL effectively helps protect sensitive data and prevent cyber threats.
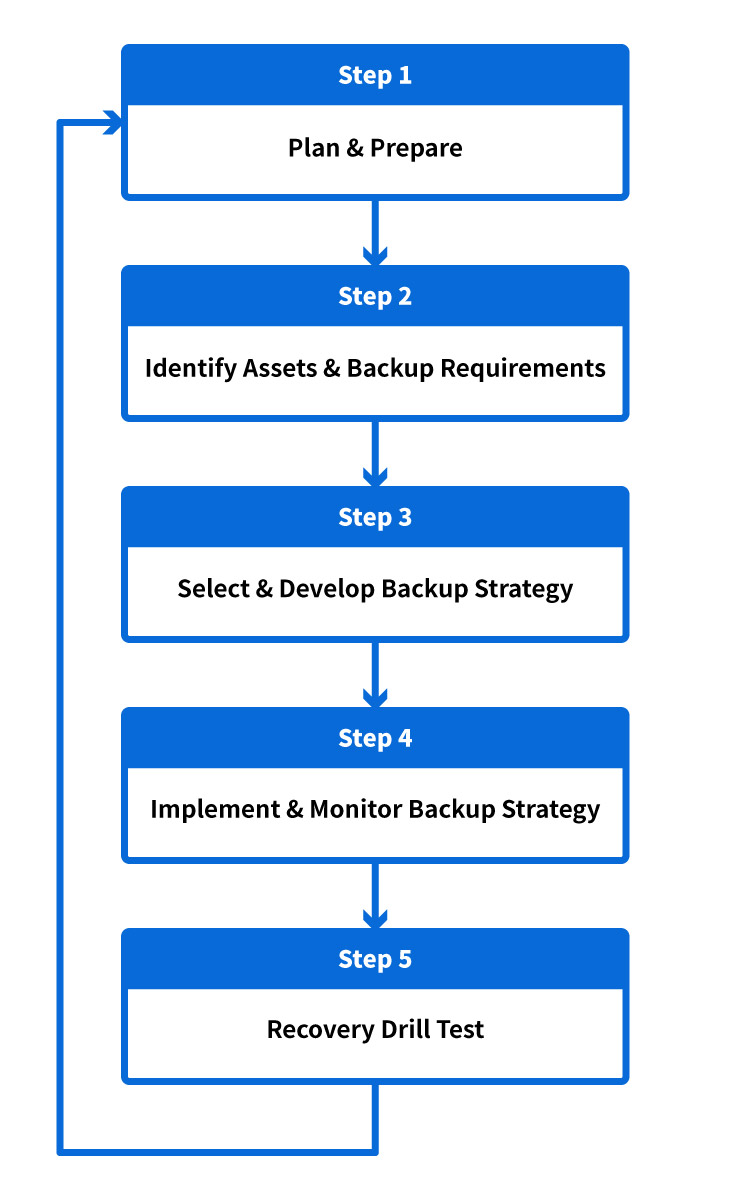
5. Backup and Recovery Strategies
Regular backups ensure data integrity and disaster recovery. Essential backup strategies include:
- Full Backups: Creating complete copies of the database at scheduled intervals.
- Incremental Backups: Storing only changes made since the last backup to save storage.
- Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR): Restoring databases to a specific time using binary logs.
- Automating Backups: Using tools like mysqldump, Percona XtraBackup, and cloud backup services.
- Testing Backup Restores: Regularly verifying backups to ensure they can be restored successfully.
Implementing a robust backup plan minimizes data loss risks and ensures business continuity.
6. Advanced MySQL Features and Scalability
For high-performance applications, advanced MySQL features help with scalability and efficiency:
- Replication: Setting up master-slave or multi-master replication for high availability.
- Sharding: Distributing large databases across multiple servers for better performance.
- Partitioning: Splitting tables into smaller partitions to optimize query speed.
- Stored Procedures and Triggers: Automating database functions for efficiency.
- Using MySQL with Cloud Platforms: Managing MySQL in cloud environments like AWS RDS, Google Cloud SQL, and Azure Database for MySQL.
Leveraging these features enables businesses to scale MySQL databases effectively.



You must be logged in to post a comment.